what is ground in electronics|ground electrical circuit : Baguio The ground is the node or point in space defined as zero volts of electric potential (not zero volts of voltage). In electromagnetic theory, it is necessary to choose a point and define as 0 V of electric potential, . For security reasons, you must log in to your Virtual Pag-IBIG Account to access your Pag-IBIG Fund savings and loan records. Continue. Welcome to the Virtual Pag-IBIG for Employers. Now, you can enjoy Pag-IBIG Fund services for your business and your employees safely and conveniently, anytime, anywhere!16,800+ FREE Online Slots Games to Play - Play free slot machines from top providers. Play with no download, no deposit, or registration!
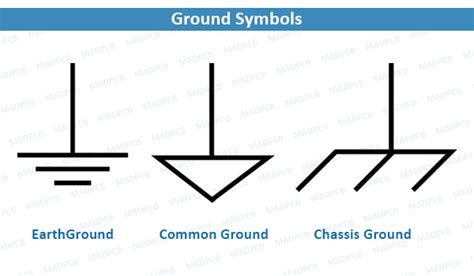
what is ground in electronics,Learn the definition and usage of ground in electronics, and how it differs from earth ground in wall outlets. See examples of circuits with ground symbols and how to connect them.what is ground in electronics ground electrical circuitIt’s common to define a zero point (0V), or ground, in a circuit. In a simple battery .Learn about earth ground, common ground, analog ground, and digital ground in electronics and electrical engineering. See how they are represented by different .In electronics and electrical engineering, “ground” is fundamental yet often misunderstood. Grounding is a crucial concept that ensures electrical systems’ safety and proper .
The ground is the node or point in space defined as zero volts of electric potential (not zero volts of voltage). In electromagnetic theory, it is necessary to choose a point and define as 0 V of electric potential, .

Learn the definitions and differences of ground, earth, and chassis in electronic design, and how to avoid common grounding problems. Find out how to use .
Ground is the reference point for all signals or a common path in an electrical circuit where all voltages can be measured. Learn how grounding works as .ground electrical circuitIn electricity supply systems, an earthing (grounding) system defines the electrical potential of the conductors relative to that of the Earth's conductive surface. The .
Ground in Circuit Analysis. In Voltage and Current we said that all voltages are relative between two points. In Electrons at Rest we explained that the electric potential function is just another way of . In electronic circuits, ground refers to a specific point in the circuit that serves as a reference level. It is used as a common connection point for various . Grounding is a wiring connection that provides a path for short circuit current to be sent to earth ground when a fault in the electrical power system occurs. In . Ground, in the context of electronics, is the reference point for all signals or a common path in an electrical circuit where all of the voltages can be measured from. This is also called the common drain since the voltage measurement along it is zero. Ground could also refer to the earth ground, literally connecting electrical equipment to .Ground as a voltage reference, physical concept, and advanced use in high-speed design, antenna ground planes, and undesired ground loops. 7 min read The concept of ground is a particularly dangerous area of .Circuit common is considered to be a separate concept, with the symbol . My understanding is that "ground" means that the node can and should be tied to the earth. "Common" implies an arbitrary voltage reference .what is ground in electronics Ground in electronic circuits refers to a specific reference point in the circuit. It is essential for providing a common voltage reference, stabilizing signals, and ensuring the proper functioning of electronic devices. Without a proper ground, circuits can experience interference, signal loss, and potential damage. An electrical ground system should have an appropriate current-carrying capability to serve as an adequate zero-voltage reference level. In electronic circuit theory, a "ground" is usually idealized as an infinite source or sink for charge, which can absorb an unlimited amount of current without changing its potential.In electronics and electrical engineering, it is by convention we define a point in a circuit as a reference point. This reference point is known as Ground (GND) and carries a voltage of 0V. Voltage measurements are relative measurements. That is, a voltage measurement must be compared to another point in the circuit. As requested by a random redditor, a short video explaining what ground is with some very simple examples. If you're a beginner, I hope this video clears up .

Traditionally, "ground" is the lowest potential in a circuit, e.g. the minus side of a battery or DC supply. In an AC circuit, such as the 110 volts AC coming into your house (at least in the US), ground will be the wire closest to the earth potential (i.e. you can usually touch the white wire, which is the ground or neutral wire, but get a bad shock if .
Traditionally, "ground" is the lowest potential in a circuit, e.g. the minus side of a battery or DC supply. In an AC circuit, such as the 110 volts AC coming into your house (at least in the US), ground will be the wire closest to the earth potential (i.e. you can usually touch the white wire, which is the ground or neutral wire, but get a bad shock if .
what is ground in electronics|ground electrical circuit
PH0 · what does a ground do
PH1 · types of electrical grounds
PH2 · is negative ground on battery
PH3 · ground in a circuit
PH4 · ground electrical circuit
PH5 · electronics ground symbol
PH6 · electrical grounding
PH7 · common ground circuit
PH8 · Iba pa